We explain what the Peace Conference of Paris of 1919 was and what were the peace treaties that were signed after World War I.

What was the Paris Peace Conference?
The Peace Conference of Paris was an encounter between the rulers of the allied countries that won in the World War I (1914-1918). It was held in the capital of France with the objective of negotiating the conditions for the drafting of peace treaties with expired nations. The defeated Nations authorities were excluded from the negotiations.
The conference opened on January 18, 1919 and was dominated by four personalities:
- Georges ClemenceauPresident of the Council of Ministers of France.
- David Lloyd GeorgePrime Minister of the United Kingdom.
- Woodrow WilsonPresident of the United States.
- Vittorio Emanuele OrlandoPresident of the Council of Ministers of Italy.
The result of the Paris Peace Conference was the signing of the Versailles Treaties (with Germany), Saint-Germain (with Austria), Neuilly (with Bulgaria), Trianon (with Hungary) and Sèvres (with Turkey), the latter replaced by the Treaty of Lausana in 1923. He also gave birth to the society of nations. The Peace Conference of Paris concluded in January 1920.
Frequent questions
Who gathered at the Paris Conference of 1919?
The Paz Conference of Paris brought together the representatives of the countries of the entente, the side that won the First World War (1914-1918) against the central empires. His main protagonists were David Lloyd George (United Kingdom), Georges Clemenceau (France), Woodrow Wilson (United States) and Vittorio Emanuele Orlando (Italy).
When did the Paris Conference begin?
The Peace Conference of Paris began on January 18, 1919, two months after the signature of the armistice with Germany that ended World War I.
What was the objective of the Paris Conference?
At the Paris Conference, the conditions for postwar peace were negotiated. On June 28, 1919, the Treaty of Versailles was signed with Germany and, during the following months, peace treaties with the other defeated countries were signed.
What agreements were taken at the Paris Conference?
The Peace Treaties with the defeated nations were signed at the Peace Conference of Paris and the pact of the Nations Society was agreed, which gave birth to the Nations Society. This international organization was the antecedent of the United Nations Organization (UN) that emerged after World War II.
- See also: PERIOD OF DELIVERY (FIRST STAGE)
The historical context
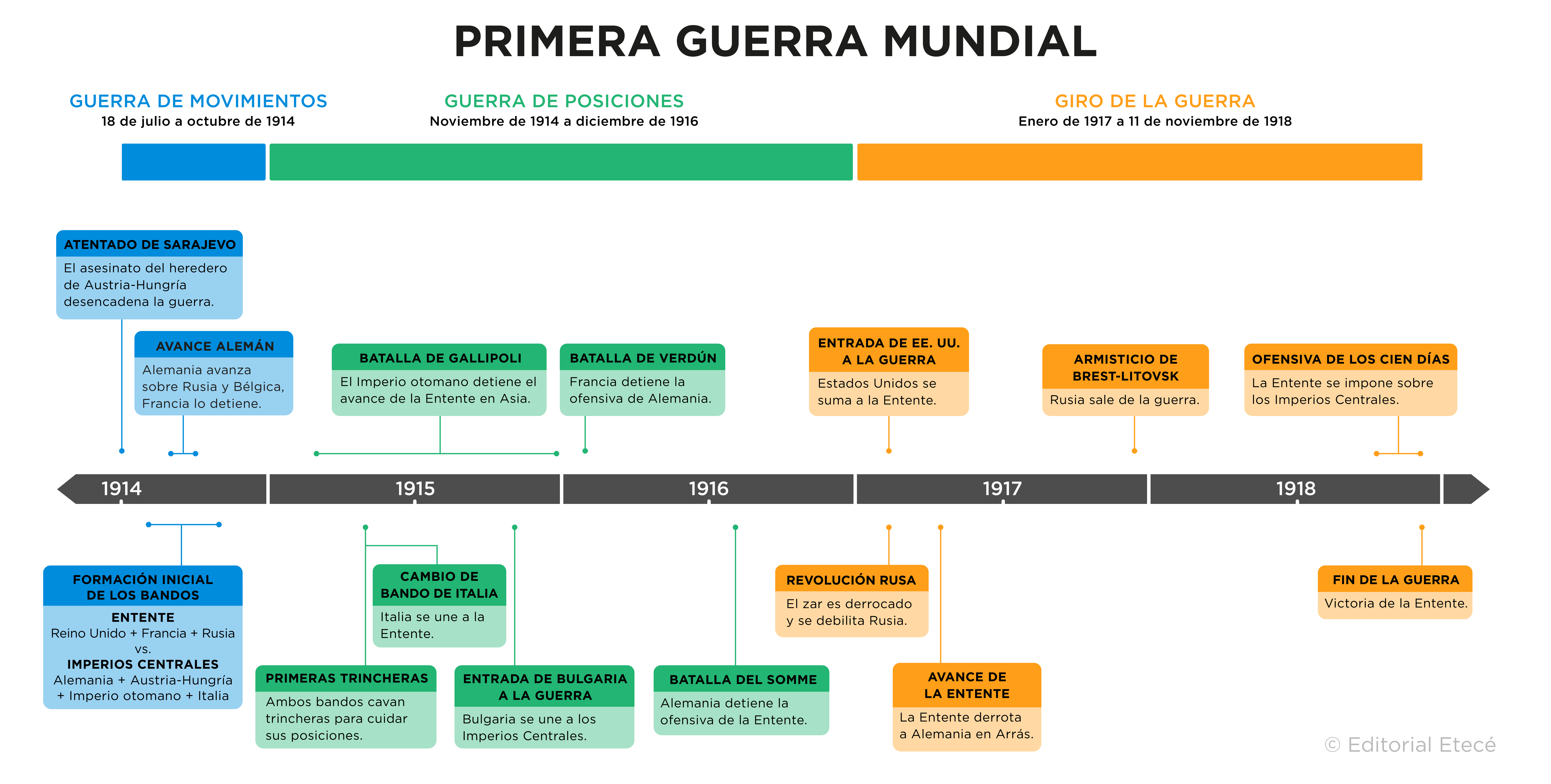
World War I ended when Germany signed the armistice on November 11, 1918. However, the conditions of peace were going to be negotiated at a conference held by the countries of the entente. The decision of the victors (headed by France, the United Kingdom, Italy and the United States) was exclude from negotiations the representatives of the defeated countries (Germany, Austria, Hungary, Bulgaria and Türkiye). The government of France insisted that Paris was the headquarters of the Peace Conference.
The president of the United States, Woodrow Wilson, arrived in December 1918 together with the rest of the US delegation. However, the conference began only on January 18, 1919 due to a delay by British Prime Minister, David Lloyd George.
Before the conference began formally, The leaders and foreign ministers of France, the United Kingdom, the United States and Italy They held preliminary meetings in which they agreed that they would concentrate decision making.
- See also: political leaders during World War
Peace treaties at the Paris Conference

At the Paz Conference in Paris 32 states participated, although the singing voice took the “great four”: Woodrow Wilson, Georges Clemenceau, David Lloyd George and Vittorio Emanuele Orlando. The defeated could not participate in the negotiations and they simply presented the treaties to sign them.
After long debates among the victors, finally The five treaties that formed “La Paz de Paris” were signed:
- Treaty of Versailles with Germany (June 28, 1919).
- Treaty of Saint-Germain with Austria (September 10, 1919).
- Neuilly Treaty with Bulgaria (November 27, 1919).
- Treaty of Trianon with Hungary (June 4, 1920).
- Treaty of Sèvres with Türkiye (August 10, 1920). This peace was rejected by the Turkish nationalist regime that, after his victorious war against the Greeks, subsequently signed the Treaty of Lausana (July 24, 1923).
Before the signing of the treaties, it had been approved at the Paris Conference The Pact of the Society of Nationsbased on Wilson's proposal to create an international association that will guarantee the peace and security of member countries.
This pact It was attached to each of the signed treaties and the Nations Society began operating in January 1920. However, the United States never integrated it due to the refusal of the representatives of the Republican party in the American Senate.
The Peace Conference of Paris concluded in January 1920, although some of the treaties were signed later.
Continue with:
- End of World War I
- Consequences of World War I
- World War I peace treaties
- PERIOD OF DELIVERY
References
- Britannica, Encyclopaedia (2023). Paris Peace Conference. Britannica Encyclopedia. https://www.britannica.com/
- Britannica, Encyclopaedia (2022). Treaty of Versailles. Britannica Encyclopedia. https://www.britannica.com/
- Cabrera, M., Juliá, S. & Martín Aceña, P. (comps.) (1991). Europe in crisis. 1919-1939. Editorial Pablo Iglesias.
- Sevillano Calero, F. (2020). The Europe of award. The disrupted order. Synthesis.
- Macmillan, M. (2017). Paris, 1919. Six months that changed the world. Tusquets





